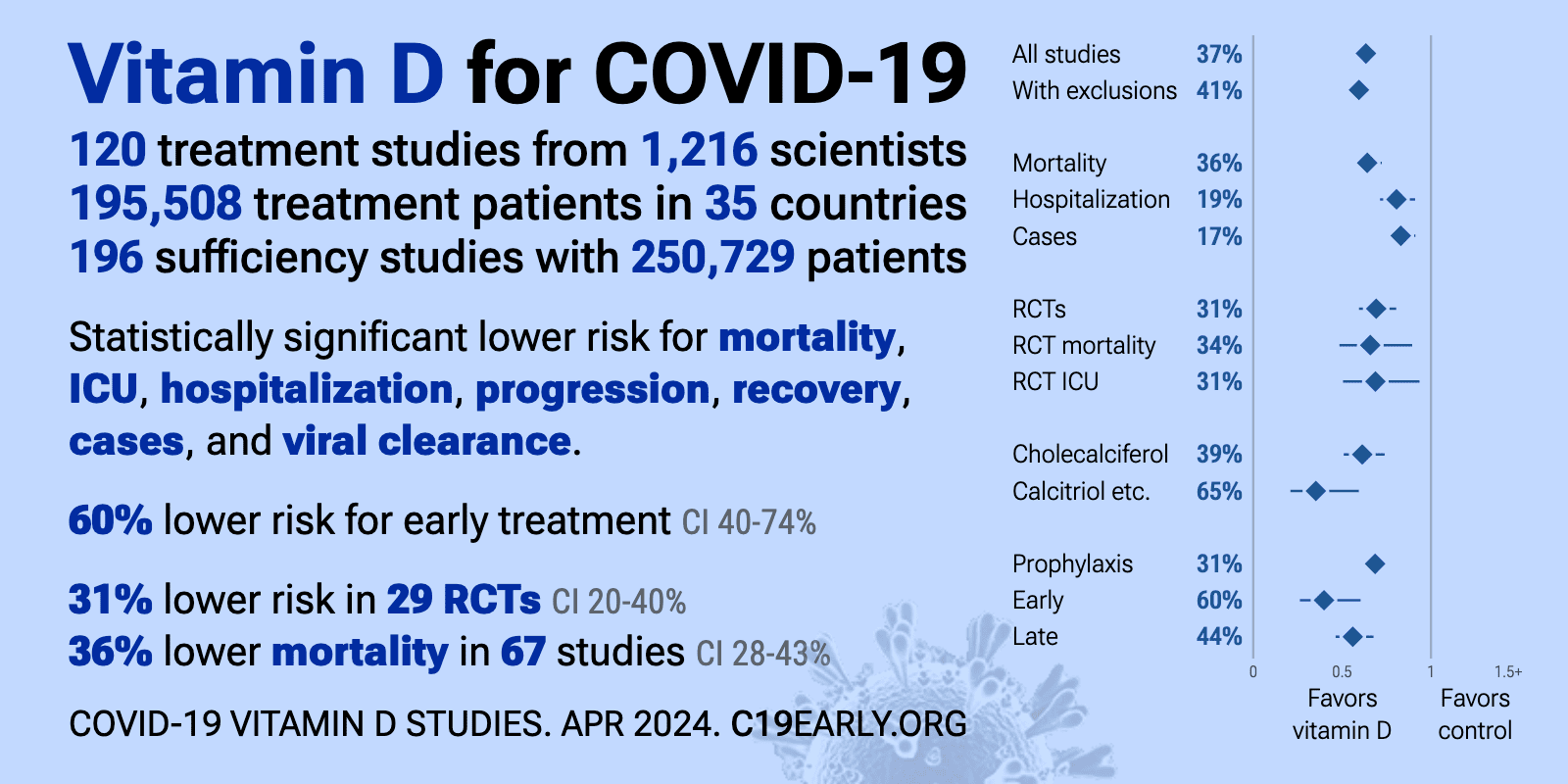
COVID ICU 3X less-likely if take any amount and type of Vitamin D – meta-analysis
Protective Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on COVID-19-Related Intensive Care Hospitalization and Mortality: Definitive Evidence from Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis
Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010130
Christiano Argano h* , Raffaella Mallaci Bocchio 1, Giuseppe Natoli1 , Salvatore Scibetta 1,
Marika Lo Monaco 1,2 and Salvatore Corrao 1
Internal Medicine Department iGR, National Relevance Hospital Trust, ARNAS Civico,
Di Cristina e Benfratelli, 90127 Palermo, Italy
Dipartimento di Promozione della Salute, Materno Infantile, Medicina Interna e Specialistica di Eccellenza "G. D'Alessandro", PROMISE, University of Palermo, 90127 Palermo, Italy
- Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +39-091-655-2065; Fax: +39-091-666-3167
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic represents one of the world's most important challenges for global public healthcare. Various studies have found an association between severe vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19-related outcomes. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune function and inflammation. Recent data have suggested a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19- related health outcomes. The purpose of this meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis (TSA) was to better explain the strength of the association between the protective role of vitamin D supplementation and the risk of mortality and admission to intensive care units (ICUs) in patients with COVID-19.
Methods: We searched four databases on 20 September 2022. Two reviewers screened the randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and assessed the risk of bias, independently and in duplicate. The pre-specified outcomes of interest were mortality and ICU admission.
Results: We identified 78 bibliographic citations. After the reviewers' screening, only five RCTs were found to be suitable for our analysis. We performed meta-analyses and then TSAs.
Vitamin D administration results in a decreased risk of death and ICU admission (standardized mean difference (95% CI): 0.49 (0.34-0.72) and 0.28 (0.20-0.39), respectively). The TSA of the protective role of vitamin D and ICU admission showed that, since the pooling of the studies reached a definite sample size, the positive association is conclusive. The TSA of the protective role of vitamin D in mortality risk showed that the z-curve was inside the alpha boundaries, indicating that the positive results need further studies.
Discussion: The results of the meta-analyses and respective TSAs suggest a definitive association between the protective role of vitamin D and ICU hospitalization.
📄 Download the PDF from Vitamin D Life
Vitamin D meta-analyses of Virus studies
This list is automatically updated
{category}
Vitamin D Life – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
{include}
- The above image is automatically updated
